CNC Machining VS 3-D Printing: Pros and Cons
As newer innovations in the manufacturing world enter the market, the two methods that are most talked about are 3D printing and CNC machining. These two manufacturing processes can provide a variety of components necessary for all industries. Yet their differences can leave customers wondering which is better for the production of their parts, components and finished products. Let’s take a look at how these two methods stack up against each other.
CNC Machining
Computer numerical control (CNC) machining has been around for more than 50 years. It is considered a subtractive manufacturing process where machines carve out the product from a large piece of material by removing the excess. CNC machining can be used for prototyping, small volume production runs and large volume production runs. The basic process involves an engineer using computer-aided software (CAD) to make either a 2D or 3D model. The model file then is made into machine instructions using a program as the program creates commands that a CNC machine will use to create the actual component.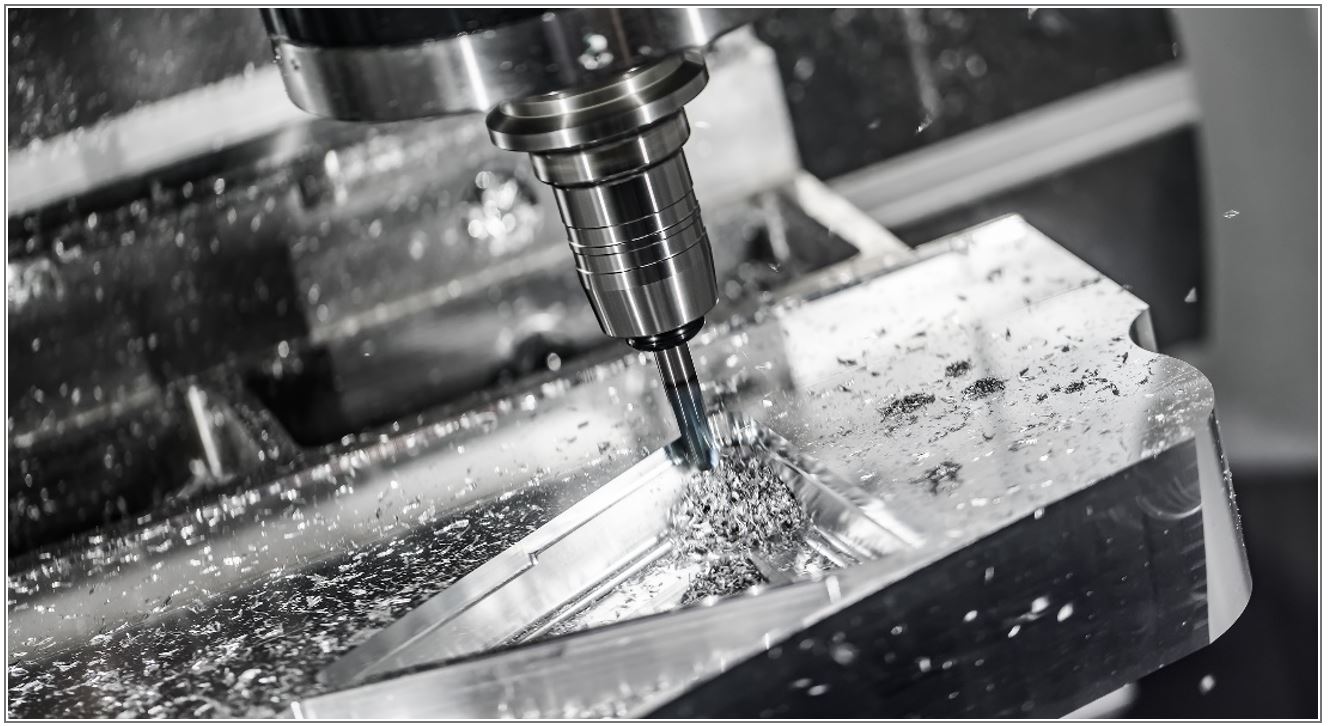
CNC machining processes use multiple types of machines such as lathes, grinders, plasma/laser cutters, mills and many others.
Pros
- Unlimited size range: CNC machining can be used to produce components in a range of sizes.
- Various material use: This method can also use a wide range of materials including metal, alloys, plastic, wax, and acrylics.
- Precision production: A CNC machine can create accuracy rates that can reach the nearest micrometer, making this a very precise process.
- Heat tolerance: CNC machines can tolerate high heat thresholds when making components.
- Fast mass production: Subtractive manufacturing is faster than additive manufacturing by simply removing materials that are not needed for the component. The process also uses several machines to create the finished product.
- Repeatability and quality: CNC machining excels at making high quality products that are repeatable for large volume runs
- Strong parts: CNC machining is usually the preferred method for parts that need to be strong and durable, such as components for airplanes.
Cons
- Waste: CNC machining does create waste. If the manufacturer has no way to reclaim and recycle this waste, it could increase the costs of the produced components.
- Incompatible files: The files created by CAD for CNC machines cannot be used for other manufacturing processes such as 3D printing.
- Costs more for smaller quantities: CNC machining prices decrease when more products are made. It is ideal for mass production for high volume runs as costs can add up for smaller volume production runs.
3D Printing
The 3D printing process is not a new technology as it was invented in the 1980s. However, it has only been in the last few decades where manufacturers have been making great strides in using it in their processes. This method is called additive manufacturing. Additive manufacturing is where a material is added onto itself to create the finished component, part or end product. The technique is done by layering the materials on top of each other from the bottom up.
Similar to CNC machining, 3D printing also uses a CAD machine to create a model file. Engineers can also use a scanner. Then a program takes the 3D model and slices it into 2D layers as it produces a G-code file that has the manufacturing instructions. This G-code file is then sent to the 3D printer to create the physical product.
There are several different ways that 3D printing creates the product based on the types of materials that are used. Selective laser sintering and selective laser melting are used primarily for metals while fused deposition modeling and stereolithography are used with plastics and polymers.
Pros
- Component complexity: 3D printing can make extremely complex geometries from a single material because of its additive manufacturing process.
- Flexibility: The 3D printing process is very flexible when it comes to switching between production jobs for small volume runs.
- Customization options: This additive method excels when making unique, customized parts for niche industries such as art, jewelry and medical.
- Cost-effective for small quantities: 3D printing per-unit prices stay stable for smaller quantity runs.
- Ideal for prototyping and smaller runs: 3D printing can speed up prototyping and smaller production runs.
- Less waste: Since it is an additive manufacturing process, it only uses the exact amount of material necessary to make the product.
Cons
- Reduced material selection: Customers cannot use 3D printing for a wide range of materials as conventional subtractive method can process
- Size limitations: A component can only be made based on the size of the printer bed. While 3D printing can create large products, each component would need to be built separately and then combined together later.
- Slower turnaround times for higher production runs: This process simply can’t keep up with higher production runs like CNC machining.
Use Impro for your Manufacturing Solutions
There are many pros and cons involved when comparing CNC manufacturing with 3D printing. While 3D printing provides some benefits to customers making prototypes and a small number of products, industries who are looking for flexibility in materials, fast turnaround times, and accurate and repeatable mass production runs can find amazing benefits with CNC machining processes. To help you decide on the best way to make your products, reach out to an expert at Impro.